No matter how long or how little you’ve used a computer, you probably have some questions about computer keyboard keys and their functions. Most computers have a keyboard as their primary means of input. Keyboards allow users to input commands into a computer by physically pushing buttons.
They are compatible with a wide range of devices, including those that use command, menu, and Graphic User Interface (GUI) styles of the computer user interface. This article provides a quick overview of the various keyboard keys and the tasks they perform.
How Does a Keyboard Work?
Capacitive switches, contact switches, magnetic reed switches, ferrite core switches, and mercury contact switches are only a few of the types of key switches used in computer keyboards. An open circuit is created when a key is pushed to complete it. After sending the signal, the keyboard’s internal processor assigns a different code to each key.
After the code has been created for a given press, it is sent to the computer’s main CPU for execution and then sent to the device’s display. When the user lets off the key they were pressing, the circuit is broken, and the cycle begins again with the next key they press.
Computer Keyboard Keys and Their Functions
What each key on a computer keyboard does is detailed below:
Alphabetic key:
The letters of the alphabet, the rows, and any special characters that may be present. A typewriter would have keys like this. The Letters of the Alphabet Are. The whole set of letters in the English alphabet (A – Z).
Number Key:
There’s a numeric keypad below the alphabetic one. These keys sit above the standard alphabetic keyset. It is possible to type punctuation and other symbols using only the numeric keypad, like as \ (backslash), | (vertical bar), / (forward slash),? (question mark), . (period/dot), > (greater than), (comma), < (less than), ; (semi-colon), : (colon), ’ (single quote/apostrophe), ” (double-quote), [ (open/left bracket), { (open/left brace), ] (close/right bracket), } (close/right bracket).
Arrow Key:
You’ll find these keys to the right of the alphabet keys. There are four subsets of keys on this keyboard, including the Left Arrow, Right Arrow, Up Arrow, and Down Arrow keys.
Numeric & Logical Key:
Almost typically, the Numeric keypad sits to the right of the main set of keys. Keys for the numerals 0 through 9 and the four arithmetic operations labeled “Logical Key” are included. Flipping the NUM LOCK key transforms the Numeric keypad into a cursor control pad.
Nowadays, the Functional Key is spaced out over the top of a standard keyboard. Typical modern keyboards feature 12 Function keys (F1 – F12).
F1:
- To access the help menu, use F1 while holding down the Windows key.
- The BIOS setup screen appears on certain older PCs.

F2:
- If you want to change anything in the currently selected cell in MS Excel, press F2.
- For a print preview in Microsoft Word, press Ctrl + F2.
- While starting, certain older systems need access to the BIOS configuration.

F3:
- If you press F3 in MS-DOS, the previous command will be repeated.
- Windows Explorer’s built-in search tool is activated.
- To make all selected text in Microsoft Word smaller, use Ctrl+F3.
- Pressing Shift+F3 causes the text to switch between upper and lower case or to capitalize the first letter of each word.

F4:
- In Microsoft Windows, pressing Alt+F4 exits the presently running program.
- The Ctrl+F4 keyboard combination is often used to exit a program’s current tab or window.

F5:
- It causes the current document window or page to be reloaded.
- By pressing Ctrl+F5, you may clear the cache and reload a website.
- It launches the slide presentation in MS-Powerpoint.

F6:
- To navigate between open Microsoft Word files, use Ctrl+Shift+F6.

F7:
- In Microsoft Word and Outlook, the F7 key is used mostly for grammar and spelling checks.
- Pressing this button will display a log of all previous commands used in the current window.

F8:
- To open the Windows starting menu, where Safe Mode is located, use the F8 key.
- A preview picture is shown for each workspace in macOS.

F9:
- Microsoft Word’s F9 key refreshes the current document.
- To communicate through Outlook email, use this shortcut key.

F10:
- During startup, press F10 to access the BIOS setup menu.
- Pressing Ctrl+F10 will make Word’s window full screen.

F11:
- Many PCs’ secret recovery partitions may be accessed by pressing Ctrl+F11.

F12:
- If you press Ctrl+F12, Microsoft Word will launch.
- Word documents may be saved by pressing Shift+F12.
- In Microsoft Word, you may print by pressing Ctrl+Shift+F12.
- Many office PCs include a shortcut key to access the Boot Menu.

Special keys on the keyboard and Their Functions:
Scroll Lock:
The Scroll Lock key has been part of the keyboard for some time. When Scroll Lock was on, navigating the page with the arrow keys took the form of a horizontal scroll rather than a vertical one.
Caps Lock:
The CAPS LOCK key prevents the alphabet keys from being used for anything except capital letters.

Num Lock:
The keyboard’s numeric keypad lights up in response to the Num Lock key. The arrows and other function keys on a number pad are the ones that work while Num Lock is depressed. A block of numerals that resembles an inverted keypad serves as the number pad.
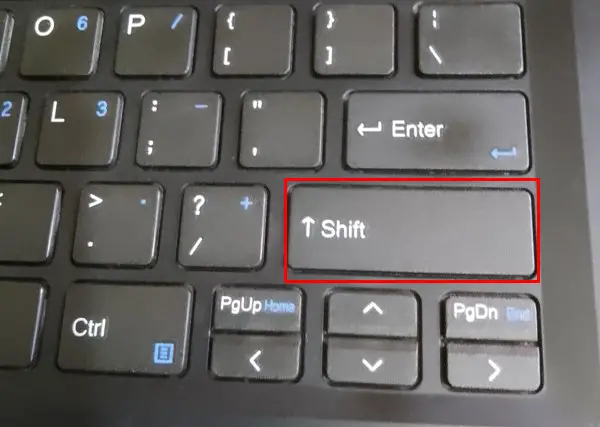
Shift:
In order to switch between a key’s lowercase and uppercase characters, the SHIFT key must be depressed and held down. When a key on a non-English keyboard has more than two characters, this method is used to access the desired special character. If you hold down this key in addition to the letter or character key, you’ll get the special character shown on the key’s lower right.
Enter:
The Enter key is the most frequently pressed key on a computer keyboard. In addition to closing a line or input in a program, the ENTER key may also be used as a trigger in a first-person shooter. The ENTER key functions similarly to the carriage return button on an electric typewriter when used with a word processor.

Space:
The key is labeled SPACEBAR, or the “white space” key. Pressing the SPACEBAR creates a single blank space character.

Backspace:
When you press the BACKSPACE key, the character that comes after it is substituted for the one that was deleted.

Ctrl:
Numerous shortcuts on the computer’s keyboard revolve around the Ctrl key.

Alt:
The Alt key is also often utilized as a shortcut in many programs.

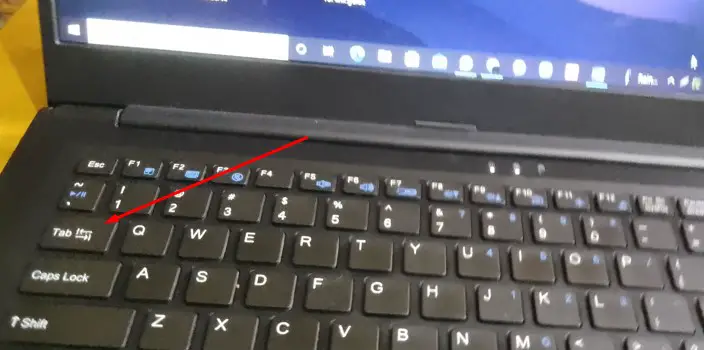
Tab:
To advance 5 characters or tab between things, use the tab key. When you press TAB, the default margin size is 0.5 inches.
Print Screen SysRq:
If you hit the Print Screen button, a screenshot of your full screen will be taken. The primary function of the Print Screen SysRq key is to capture full-screen images.

Pause Break:
If the software allows it, pressing this key will halt the current screen from updating or a program from doing an operation. The alternative mode of this key disrupts or stops some software programs, usually, MS-DOS commands and applications, when used in conjunction with the CTRL key. To cancel an action, use Control + Break simultaneously (or Control + C).
ESC:
Most programs allow you to depart with the Escape key activated. It’s also used in conjunction with other keys to denote different actions or generate unique key values. In Windows, you may dismiss a context menu by using the ESC key.

Insert:
This inserts key toggles between two different typing styles. In the first setting, your text will display ahead of the cursor and will shift any subsequent text to the right. When you switch to the second mode, anything you enter will immediately replace whatever is on the opposite side of the cursor.
Delete:
Any data, file, media, etc. may be removed using this delete key.
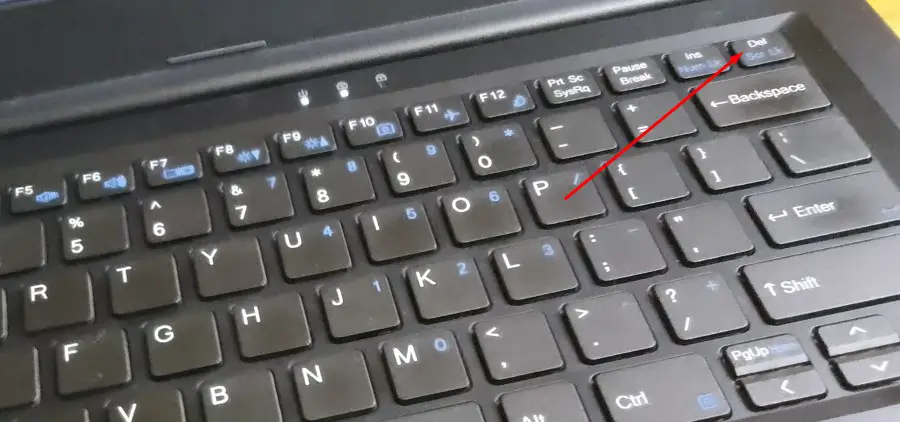

Home:
When you press the Home key, the pointer moves back to the top of the current line. The starting point of a document or cell may be selected using this key.
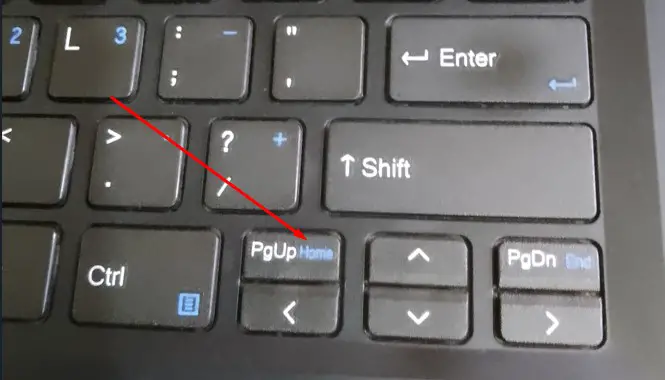
Page Up:
If the document on which you are now working contains more than one page, pressing the Page Up key will advance you by one page.
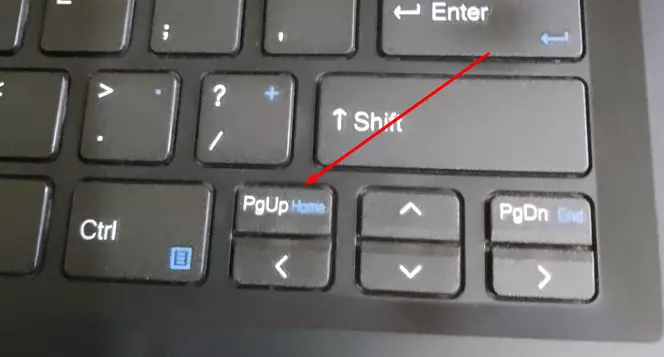
Page Down:
If the document you’re working on contains more than one page, pressing Page Down will take you down to the next available page.
End:
When you press the End key, the cursor jumps to the end of the current line.

Windows Key:
Most modern keyboards contain three additional Windows keys to the left and right of the SPACEBAR for quick access to common Windows functions.

Multimedia Key:
A multimedia key is a specialized key that may be used for several sorts of amusement. However, such keys are not standard on most standard 104-key keyboards. including Mute, Volume Up/Down, Media Player, and Play/Pause.
Internet Key:
A dedicated Internet key expedites the launch of Internet Explorer. In any case, we may put those keys to use on the web.
FAQs
What is the function of Ctrl-A to Z?
List of all the functions of Control and alphabet keys:
Ctrl+A: Select every word
Ctrl+B: makes text bold.
Ctrl+C: Text Copy
Ctrl+D: Opens the font formatting window
Ctrl+E: to center the text
Ctrl+F: Find an expression
Ctrl+G: Navigate to a certain page
Ctrl+H: Substitute text with an alternative text
Ctrl+I: Italicize text
Ctrl+J: Justify text
Ctrl+K: Open the Insert Hyperlink window
Ctrl+L: Text is aligned to the left.
Ctrl+M: Left-align the paragraph’s indentation.
Ctrl+N: Open a new file or document
Ctrl+O: Launch a previously saved file or document
Ctrl+P: Print an item.
Ctrl+Q: Delete formatted paragraphs
Ctrl+R: Align text to the right.
Ctrl+S: Save the file or document
Ctrl+T: Make a hanging indent
Ctrl+U: Underline a text selection
Ctrl+V: Paste any copied text or object.
Ctrl+W: Close a Word document or an open tab in a browser.
Ctrl+X: Cuts text or an object.
Ctrl+Y: Undo any action and redo it.
Ctrl+Z: Reverse any action.
What are Ctrl C and Ctrl Z used for?
To copy text or a picture, use Ctrl C, and to undo an activity, press Ctrl Z.
Final Words
Even though we use keyboards often, we may not be aware of all the functions each key can do. Hopefully, you’ll gain some insight and learn some new keyboard shortcuts from this piece on Computer keyboard keys and their function.

I am a regular user of computer keyboards. For using keyboard face different kinds of problems and also solve it very easily. I love sharing knowledge about keyboards.
